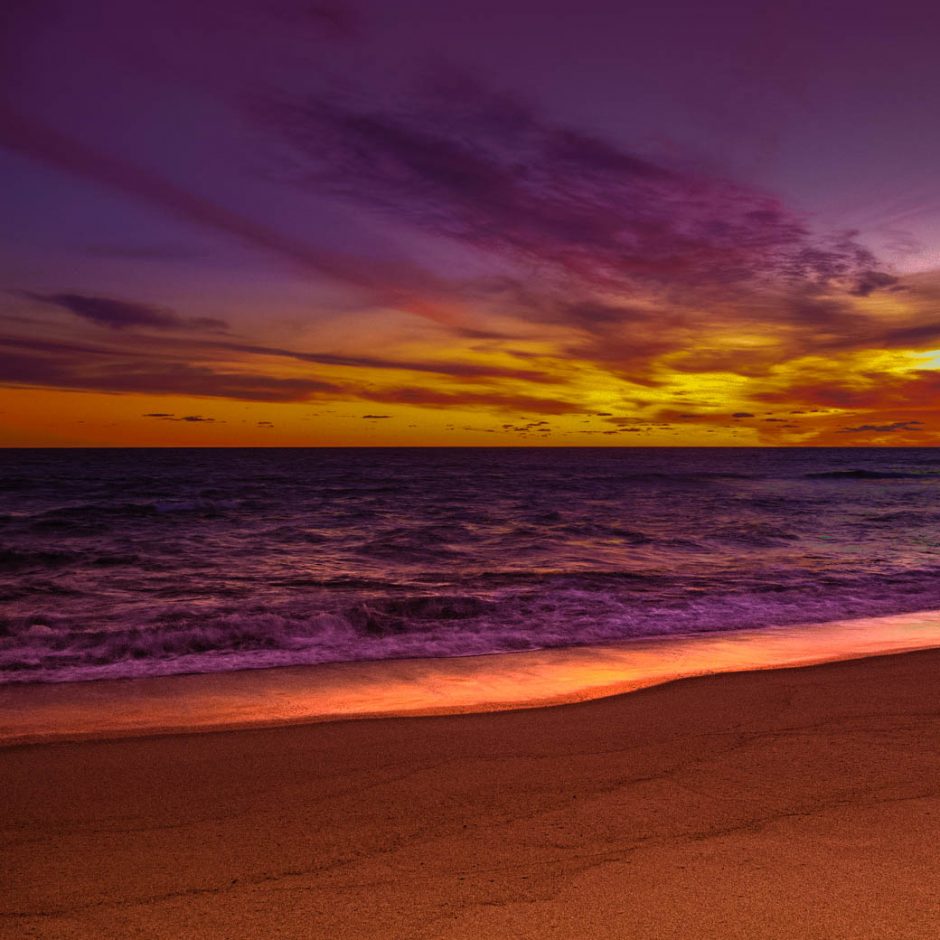
Posted on August 2, 2019 by nick - Art Cape Cod
Posted on August 1, 2019 by nick - Art Cape Cod
Posted on July 1, 2019 by nick - Uncategorized
Posted on July 1, 2019 by nick - Uncategorized
Posted on July 1, 2019 by nick - Art Cape Cod
Posted on June 15, 2019 by nick - Uncategorized
Posted on May 19, 2019 by nick - Uncategorized
Posted on January 1, 2019 by nick - Uncategorized
Posted on December 9, 2018 by nick - Uncategorized
Posted on September 20, 2018 by nick - Uncategorized
Posted on August 25, 2018 by nick - Uncategorized